What is Slope Stability Study?
Slope stability study involves the assessment of slopes to determine their likelihood of failure under various conditions. It is crucial for ensuring the safety and sustainability of infrastructure located in hilly or mountainous regions.
Kinematic Analysis
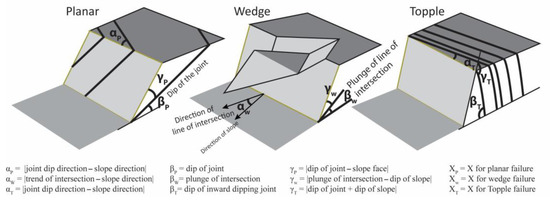
Kinematic analysis evaluates the potential for planar, wedge, or toppling failures based on the orientation of discontinuities and slope face. It uses stereonets to visualize and assess failure mechanisms (Image is credited to MDPI).
- Planar Failure: Occurs when a discontinuity plane dips toward the slope at an angle less than the slope angle but greater than the friction angle.
- Wedge Failure: Results from the intersection of two discontinuities, forming a wedge that slides along the slope.
- Toppling Failure: Happens when columns of rock overturn due to gravity and forces acting on steeply inclined discontinuities.
Limit Equilibrium Analysis
Limit equilibrium analysis determines the stability of slopes by calculating the factor of safety (FoS), which is the ratio of resisting forces to driving forces (Image is credited to Researchgate). Methods include:
- Swedish Circle Method (Fellenius): A simplified approach assuming circular slip surfaces.
- Bishop's Simplified Method: Considers both moment and force equilibrium for circular slip surfaces.
- Janbu's Method: Suitable for non-circular slip surfaces and complex slope geometries.

Applications
- Assessing the stability of natural and man-made slopes
- Designing retaining walls and slope reinforcement systems
- Evaluating landslide risks and proposing mitigation measures
- Planning and executing mining and excavation projects
Advantages
- Provides insights into slope behavior and potential risks
- Helps optimize design and construction for safety and cost-effectiveness
- Supports sustainable development in geologically challenging terrains
Limitations
- Requires detailed geological and geotechnical data
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive for complex slopes
- Results may vary based on assumptions and selected methods