What is Seismic Refraction?
Seismic refraction is a geophysical method used to investigate subsurface structures. It involves measuring the travel time of seismic waves refracted at the interfaces between different subsurface layers (Image is credited to Brantax).

Basic Principle
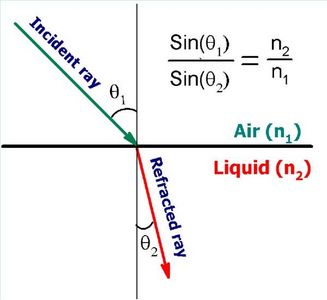
The seismic refraction method is based on Snell's Law, which describes the bending of seismic waves as they pass through materials of varying densities and velocities. A seismic source generates waves that travel through the subsurface and are refracted back to the surface at critical angles (Image is credited to Moodle).
Key Components
- Seismic Source: Generates the seismic waves (e.g., hammer, explosives).
- Geophones: Detect the returning seismic waves.
- Recording Equipment: Captures and stores the seismic data for analysis.
Applications
Seismic refraction surveys are widely used in engineering, environmental studies, and exploration. Common applications include:
- Determining depth to bedrock
- Mapping subsurface layers
- Identifying groundwater or voids
Advantages
- Non-invasive and cost-effective
- Provides valuable subsurface information
- Useful in various soil and rock types
Limitations
- Requires significant contrasts in material velocities
- Limited depth penetration compared to seismic reflection
- Affected by surface noise and other interferences