What is MASW?
Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) is a geophysical method used to evaluate subsurface stiffness by analyzing surface wave propagation. It is particularly effective for shallow investigations.
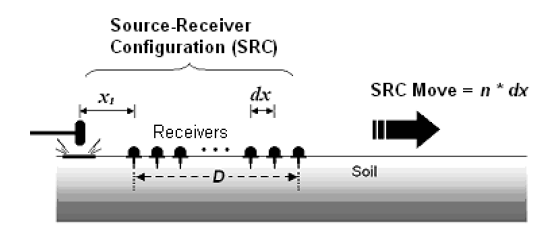
Basic Principle
MASW utilizes surface waves, such as Rayleigh waves, which are generated by a seismic source. The method involves analyzing the dispersion characteristics of these waves to derive a shear wave velocity profile of the subsurface (Image credited to Researchgate).

Key Components
- Seismic Source: Generates surface waves (e.g., sledgehammer, weight drop).
- Geophones: Array of sensors to capture wave propagation.
- Recording Equipment: Collects and stores waveforms for processing.
Applications
MASW is widely used in geotechnical engineering, environmental studies, and subsurface profiling. Common applications include:
- Determining shear wave velocity profiles
- Assessing soil stiffness and dynamic properties
- Detecting subsurface anomalies
Advantages
- Non-invasive and quick to deploy
- Provides continuous stiffness profiles
- Effective in diverse soil and rock conditions
Limitations
- Limited depth penetration in high-frequency surveys
- Requires a sufficiently large source-to-receiver distance
- Dependent on accurate dispersion curve analysis